FCC Gasoline Selective Desulfurization Catalysts
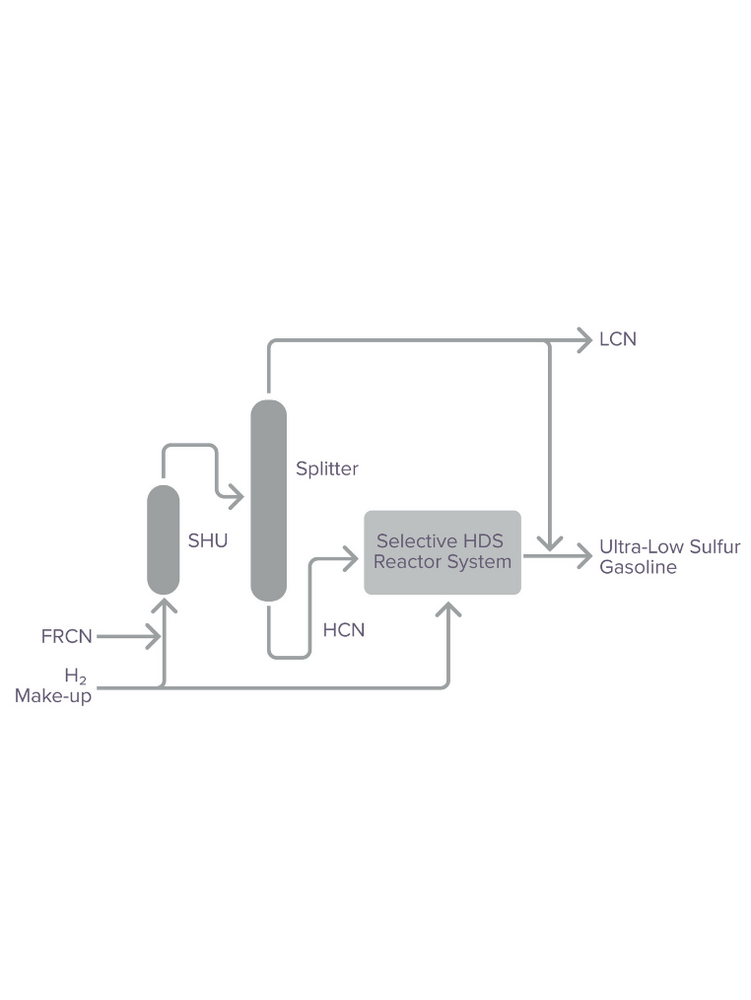
The catalytic system, developed by Axens, allows achievement of ultra-low-sulfur gasoline targets by complete control of mercaptan species along the different steps of the process, while protecting the HDS section from pressure drop buildup and poisoning.
As the world leader in the field of selective FCC naphtha desulfurization, Axens offers tailored catalytic solutions. Due to an optimized metal content and highly neutral carrier, FCC gasoline HDS catalysts present very low sensitivity to impurities and excellent activity, stability, selectivity and regenerability. While octane retention is maintained over time, this ensures the longest cycle length between two turnarounds with no risk of intermediate shutdown, as well as extended cycle life.
With an unmatched experience of more than 300 Prime-G+® references worldwide, one third of gasoline produced worldwide today is treated by catalyst in Axens’ FCC gasoline HDS family.
HR 845
HR 845 is the catalyst of choice used in Prime-G+® FCC Selective Desulfurization Technology to eliminate light sulfur compounds from cracked naphthas. It provides high level of sulfur removal to meet the new specifications of motor gasolines.
HR 845 can be delivered under ready-to-use presulfided form.
HR 855
HR 855 is a recently-developed catalyst used in the Prime-G+® technology and has been specially designed to eliminate light sulfur compounds from cracked naphthas.
It provides high level of sulfur removal in light FCC gasoline fractions to meet the ultimate specifications of motor gasolines (< 10 wppm sulfur). This performance combines a complete removal of diolefins and a very limited hydrogenation of olefins (octane preservation).
HR 855 can be delivered under ready-to-use presulfided form.
HR 806
HR 806 intrinsic selectivity allows the achievement of ultralow sulfur product with minimum octane penalty. Itsneutral carrier provides good stability and ensures long cycles.
HR 806 can be delivered under ready-to-use presulfided form.
HR 846
HR 846 optimized formulation allows to achieve a significantly higher level of sulfur removal with minimum octane penalty due to its enhanced activity. Its neutral carrier and its high resistance to contaminants provides a good stability and ensures long cycles.
HR 846 can be delivered under ready-to-use presulfided form.
HR 856
HR 856 outstanding selectivity and high activity allow the achievement of ultra-low sulfur product with minimum octane penalty. Its specific carrier provides good stability and ensures long cycles.
HR 856 can be delivered under ready-to-use presulfided form.
HR 866
HR 866 outstanding activity and high selectivity allow the achievement of ultra-low sulfur product with minimum octane penalty. Its specific carrier provides good stability and ensures long cycles.
HR 866 can be delivered under ready-to-use presulfided form.
HR 841
Associated with HR 806 catalyst or HR 856/866 catalyst in Axens Prime-G+® Technology, HR 841 produces Ultra Low Sulfur gasoline with very low sulfur with a very limited reduction of the octane number.
HR 841 can be delivered under ready-to-use presulfided form.
You Might Be Interested In
Arsine Management
Silica Management
TO CONTACT US
Please fill in the contact form below